-
Technical Articles
-
- MSFS 2024 Meets GeoBox M813: The Ultimate Guide to Immersive Flight Simulation
- How to use ChromeBox for Immersive display
- How To Enhance Museum Visual Experience with Immersive Projection Technology
- S902, Improve the effectiveness of your large display system
- Perfecting Large Wall Displays
- A Guide for Effortless Immersive Experience Setup in 5 Minutes
- The Synergy of Using BrightSign Player with GeoBox video Controller
- Seamless Edge Blending: GeoBox's Black Level Uplift Solution for AV Professionals
- GeoBox New 810 Series: Elevating Pro AV Excellence
- Synergy of Digital Signage Player and Video Controller
- HDMI Technologies and Cables: A Guide for Professional AV Technicians
- Unveil GeoBox mini edge blending and warping box: G111 / G112
- The new range of All-In-One edge blending solutions - M810 series
- GeoBox in ISE2022
- G901, all-round multi-purpose controller: Multi-viewer, ultra-high resolution, 3D, Seamless switching & more..
- A better solution for your multi-projector edge blending project
- 8K input timing support in all GeoBox solutions
- How to display a large image using multiple projectors?
- Epson x GeoBox 8K/4K demo event
- 4K projectors edge blending and warping
- 4K projector edge blending, warping controller
- Immersive display solution
- How to plan for a large projection system?
- GeoBox G901 4K60hz input and output processor is now available in Europe
- Projection mapping for museum
- Projection mapping technology from GeoBox
- Edge blending calculator for multi-projector project planning
- Reliable Hardware-Based Video Processing for Professional AV Installations
- Show all articles (13) Collapse Articles
-
- How to use ChromeBox for Immersive display
- Digital art for Karuizawa New Art Museum's special exhibition"Irreplaceable Things - Earth, Landscape, and Environment"
- S902, Improve the effectiveness of your large display system
- Perfecting Large Wall Displays
- The Synergy of Using BrightSign Player with GeoBox video Controller
- Synergy of Digital Signage Player and Video Controller
- HDMI Technologies and Cables: A Guide for Professional AV Technicians
- GeoBox in ISE2022
- G901, all-round multi-purpose controller: Multi-viewer, ultra-high resolution, 3D, Seamless switching & more..
- 8K input timing support in all GeoBox solutions
- 4K in-out Video wall controller with Multi-viewer - 'world first'
- Video wall controller: Top 5 reasons why using it
- GeoBox G901 4K60hz input and output processor is now available in Europe
-
News Letters
-
Reference cases
-
- Esports AV Integration at Its Best: GeoBox Powers the ZOWIE Gaming Experience Center
- Elevating Immersive Art to New Heights: GeoBox in Hyundai Futurenet’s Le Space
- GeoBox Transforms Interior Design through Immersive Technology (Andalusia, Spain)
- Lifesize Plans - Revolutionizing Architectural Visualization
- Immersive Fusion: The Technological Creativities of Ragdale Hall Spa's Thought Zone
- Illuminating Hope: The Hanbit Tower Christmas Project of (Korea, 2020)
- GeoBox Projection Mapping in Japan Kyoto Kodai-ji Temple
- Elevating the Shopping Experience: IKEA's Immersive Technology in the Heart of Paris (France)
- 125 years BOSCH in the UK: Powered by GeoBox and Panasonic
- Sony Professional Display at OMR 2023 (Hamburg, Germany)
- The Holodeck: A Futuristic Meeting Space
- How G413 elevate guest experience at the luxurious Andreus Resorts
- Immersion in Yoga studio
- GeoBox adds edge-blending interaction to Vodafone’s flagship store in Netherland
-
- Rediscovering the Skies: Flight Simulator Brought to Life with GeoBox Technology
- Unlocking the Future of Learning
- Projection Based Immersive Learning: NOW and The Future of Education and Training
- GeoBox Unveiling the Future of Neurosurgery with 3D Technology: Interview Professor Wolfsberger (Austria)
- Creating large projection in School Theater for multiple purposes (Netherlands)
- Secta Immersive Enhances Trainings in Immersive Rooms with GeoBox
-
- GeoBox and Panasonic Projectors Immersify Kuala Lumpur
- Elevating Immersive Art to New Heights: GeoBox in Hyundai Futurenet’s Le Space
- Immersive Multimedia Installation at Museo del Lago – Montemurro (Italy)
- Digital art for Karuizawa New Art Museum's special exhibition"Irreplaceable Things - Earth, Landscape, and Environment"
- How To Enhance Museum Visual Experience with Immersive Projection Technology
- Museums in the Digital Era: Tackling Challenges and Learning from Teylers Museum (NL)
- GeoBox Enhancing Historical Landmarks with Immersion: Fort Victor Emmanuel (France)
- A Journey into Immersive Aquarium: The Deep (Hull, UK)
- 125 years BOSCH in the UK: Powered by GeoBox and Panasonic
- Immortalizing Media Heritage In the Media Museum (Hilversum, NL)
- Media museum Sound & Vision in the Netherlands
- Dive Into History with Geobox (Brugge, Belgium)
- Immersive projection installation in Switzerland
- GeoBox support Slovakia Pavilion in EXPO2020
- Experience F-16 at National Military Museum (Soest, Netherlands)
- Mori Building Digital Art Museum: Epson teamLab Borderless
- The 10th annual Korea Gyeongju World Culture Expo
- Projection mapping for museum
- GeoBox recreates the Fifth Aztec Sun at Stuttgart’s Linden Museum
- Discovering the image control solution behind Digital Art Museum
- Show all articles (5) Collapse Articles
-
Understanding and Preventing Floating Voltage in AV Systems
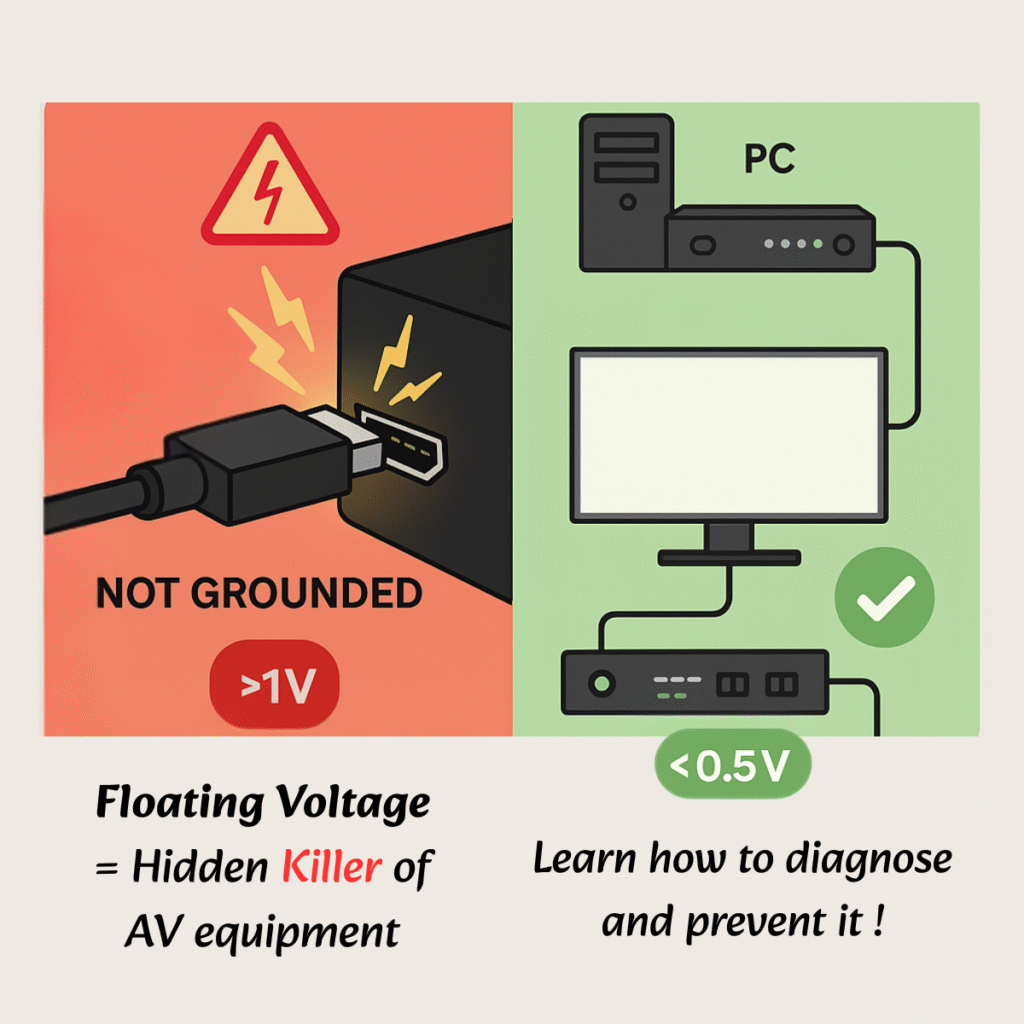
Understanding and Preventing Floating Voltage in AV Systems
A Technical Guide for Safe connectivity and System Protection
What Is Floating Voltage?
Floating voltage refers to an undefined or unstable electrical potential between two devices that are not properly grounded or powered from the same source. This condition often occurs when AV devices like PCs, media players, projectors, or video processors are connected using HDMI or other signal cables without sharing a common ground.
When a device with a different ground potential is connected via HDMI or similar interfaces (Display ports, USB or USB type-C), the voltage difference can cause a surge of current across the connection, which may result in:
- Instant IC burnout (input/output chips)
- Power supply module failure
- Permanent hardware damage to ports or circuit boards
- Unexpected shutdowns or display malfunctions
⚠️Why Is This a Common but Overlooked Issue?
Many users and even some system integrators overlook floating voltage because:
- Modern buildings often have inconsistent or unverified grounding
- Ground loops and power phase mismatches are invisible until damage occurs
- HDMI is often seen as a “low-voltage” signal interface, so risks are underestimated
- Low-cost adapters (e.g., HDMI audio extractors) often lack protection/isolation
- Floating voltage cannot be seen—only measured with proper tools

Part 1: How to Diagnose Floating Voltage Issues
Step 1: Measure Voltage Between Connector Shield and Ground
Tools: Digital Multimeter (DMM) or voltage test pen
Procedure:
- Set the multimeter to DC voltage mode.
- Connect the black probe to a known earth ground (e.g., grounded socket or metal chassis of grounded AV equipment).
- Touch the red probe to the HDMI outer metal shell of the PC or media source.
- Safe range: < 0.5V
- If > 1V, floating voltage is likely present.
👉 No multimeter? Use a small voltage test pen for approximate detection.
Step 2: Compare Ground Potential Between Devices
-
Measure voltage between:
- PC HDMI shield ↔ GeoBox HDMI input shield
- PC chassis ↔ projector/display chassis
- PC chassis ↔ HDMI splitter housing
-
A voltage difference > 1V suggests dangerous potential mismatch.
Step 3: Verify Grounding
- Is the PC plugged into a properly grounded outlet?
- Use a socket tester to check for grounding errors.
Step 4: Watch for Warning Signs
- Audible click or pop when inserting HDMI?
- Devices fail after basic re-connection?
- HDMI ports stop working after hot-plugging?
- These are classic signs of floating voltage discharge.
Part 2: How to Prevent Floating Voltage Damage
✅ 1. Ensure Proper Grounding
- Always use three-prong, grounded power outlets.
- Avoid ungrounded extension cords or cheap adapters.
- Use a UPS or power conditioner with a ground indicator when in doubt.
✅ 2. Use HDMI Isolators
- Install galvanic isolators or HDMI surge protectors between devices with separate power sources.
- These devices block ground loop current while maintaining full signal integrity.
- Recommended brands include: HDFury, Lindy, Kramer, etc.
✅ 3. Power All Equipment from the Same Circuit
- Connect your PC, display, GeoBox, and splitter to the same power strip or wall outlet.
- This ensures all devices share a common ground.
✅ 4. Pre-Ground HDMI Connectors
- Before plugging in HDMI, touch the metal connector shell to the receiving device chassis to discharge static safely.
✅ 5. Manually Ground the PC (if needed)
- If you’re unsure whether the PC is grounded, connect a ground wire from the PC chassis to a grounded rack or AV frame.
Summary
Floating voltage is a preventable but serious risk in AV systems. By taking a few proactive steps: measuring voltage, ensuring grounding, using isolators, and connecting devices properly, you can protect your equipment, reduce downtime, and avoid costly repairs.
Protect your investment. Always check before you connect.